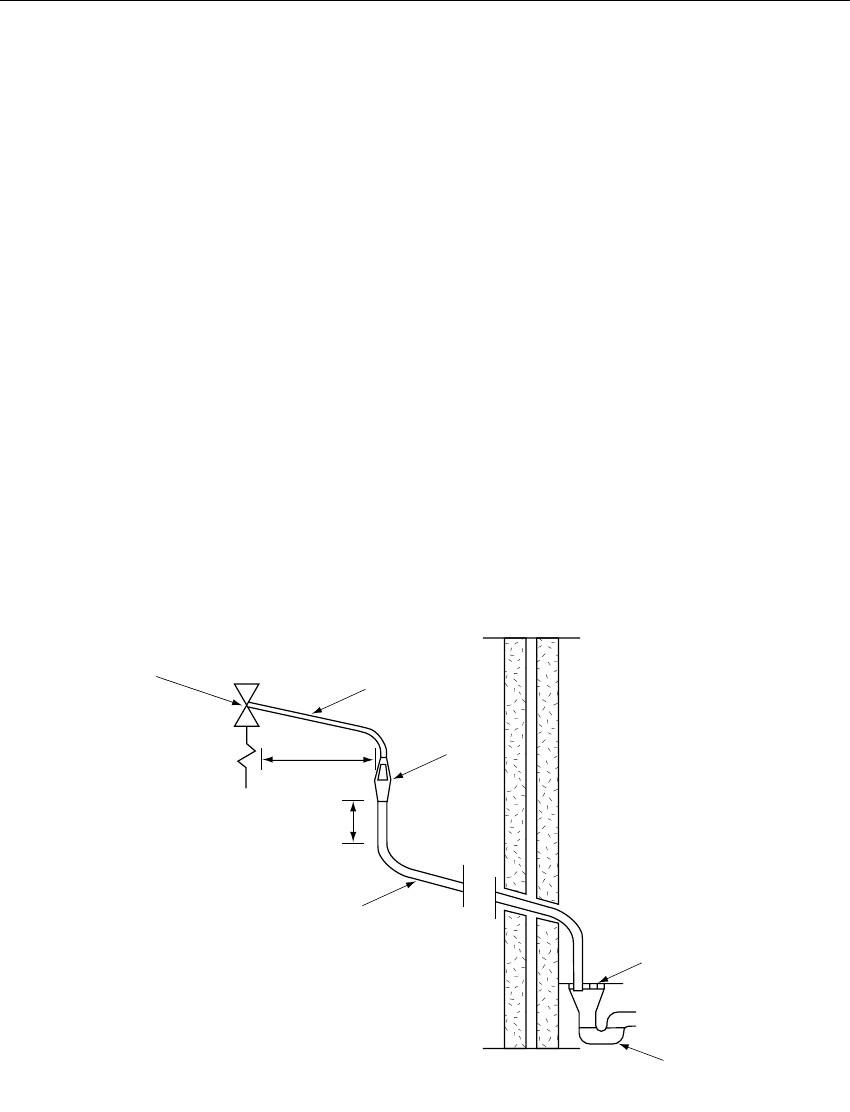
3) The pipe diameter must be at least one pipe size larger than the nominal outlet size
of the safety device unless it’s total equivalent hydraulic resistance exceeds that of a
straight pipe 9 m long.
i.e. Discharge pipes between 9 m and 18 m equivalent resistance length should be at
least 2 sizes larger than the nominal outlet size of the safety device. Between 18
m and 27 m at least 3 times larger, and so on.
Bends must be taken into account in calculating the flow resistance.
See fig..5 and Table 2.
4) The discharge pipe must have a vertical section of pipe at least 300 mm in length,
below the tundish before any elbows or bends in the pipe work.
5) The discharge pipe must be installed with a continuous fall.
6) The discharge must be visible at both the tundish and the final point of discharge,
but where this is not possible or practically difficult; there should be clear visibility at
one or other of these locations. Examples of acceptance are:
i) Ideally below a fixed grating and above the water seal in a trapped gully.
ii) Downward discharges at a low level; i.e. up to 100 mm above external surfaces
such as car parks, hard standings, grassed areas etc. These are acceptable providing
that where children may play or otherwise come into contact with discharges, a wire
cage or similar guard is positioned to prevent contact, whilst maintaining visibility.
iii) Discharges at high level; i.e. into a metal hopper and metal down pipe with the
end of the discharge pipe clearly visible (tundish visible or not). Or onto a roof capable
15
600 mm Max.
Min.
to tundish.
with continuous fall. See Table 2 and worked
of discharge).