ENGLISH
31
• Set the front speakers, center speaker
and subwoofer in the same positions as
in example (1).
• It is best to place the surround speakers
directly at the side or slightly to the front
of the viewing position, and 60 to 90 cm
above the ears.
• Same as surround back speaker
installation method (1).
Using dipolar speakers for the surround back speakers as well is more
effective.
• Connect the surround speakers to the surround speaker jacks.
• The signals from the surround channels reflect off the walls as shown on
the diagram at the left, creating an enveloping and realistic surround sound
presentation.
For multi-channel music sources however, the use of bipolar or dipolar
speakers mounted at the sides of the listening position may not be
satisfactory in order to create a coherent 360 degree surround sound field.
Connect another pair of direct radiating speakers as described in example
(3) and place them at the rear corners of the room facing towards the prime
listening position.
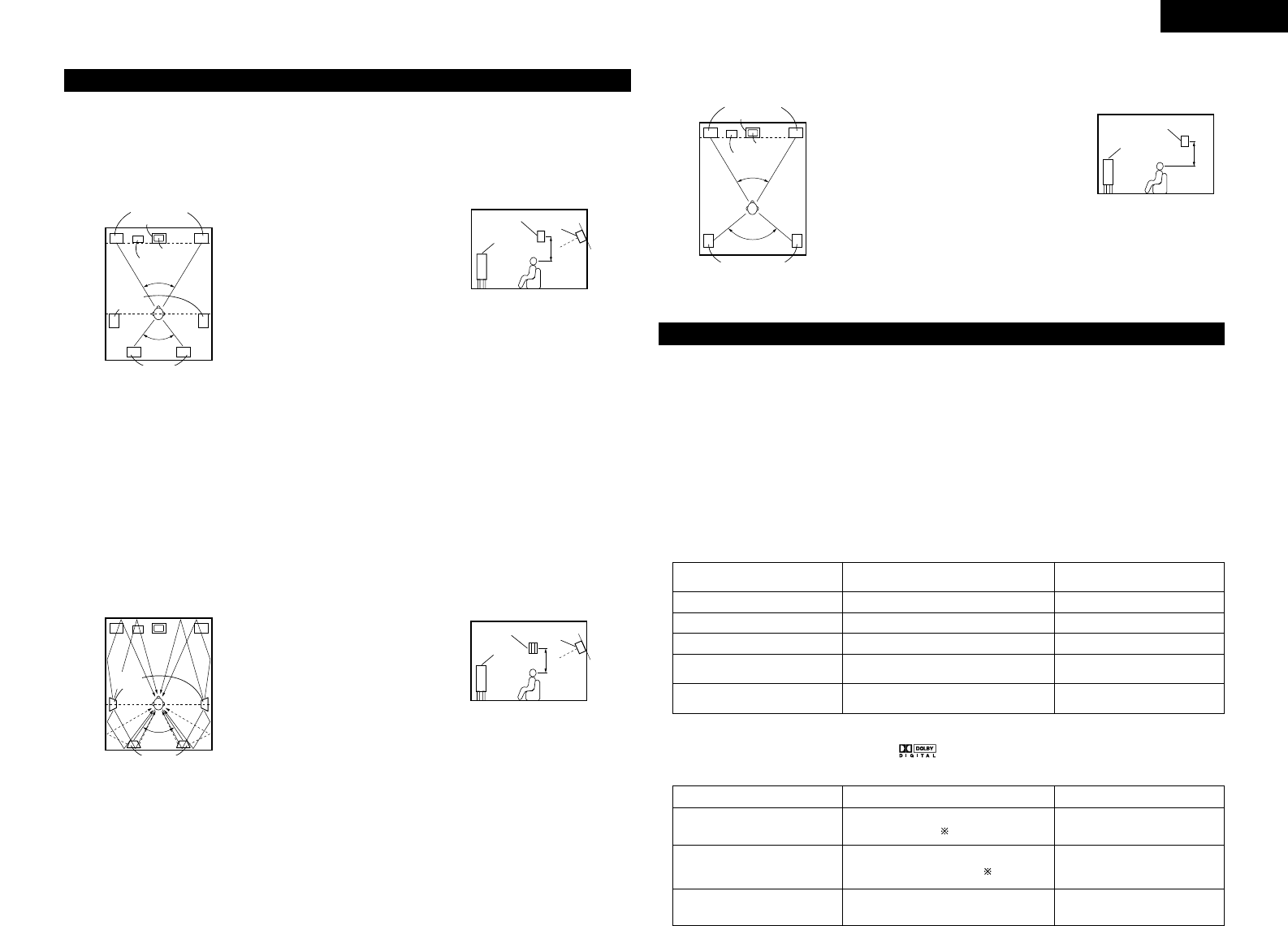
• Set the front speakers with their front
surfaces as flush with the TV or monitor
screen as possible. Set the center
speaker between the front left and right
speakers and no further from the
listening position than the front speakers.
• Consult the owner’s manual for your
subwoofer for advice on placing the
subwoofer within the listening room.
• If the surround speakers are direct-radiating (monopolar) then place them
slightly behind and at an angle to the listening position and parallel to the
walls at a position 60 to 90 centimeters above ear level at the prime
listening position.
• When using two surround back speakers, place them at the back facing the
front at a narrower distance than the front left and right speakers. When
using one surround back speaker, place it at the rear center facing the front
at a slightly higher position (0 to 20 cm) than the surround speakers.
• We recommend installing the surround back speaker(s) at a slightly
downward facing angle. This effectively prevents the surround back
channel signals from reflecting off the monitor or screen at the front center,
resulting in interference and making the sense of movement from the front
to the back less sharp.
(2) Setting for primarily watching movies using diffusion type speakers for the surround speakers
For the greatest sense of surround sound envelopment, diffuse radiation speakers such as bipolar
types, or dipolar types, provide a wider dispersion than is possible to obtain from a direct radiating
speaker (monopolar). Place these speakers at either side of the prime listening position, mounted
above ear level.
Subwoofer
Surround speaker
Front speaker
60 to 90 cm
Surround back speakers
(1 spkr or 2 spkrs)
60°
Front speakers
60°
Monitor
Center speaker
As seen from above
As seen from above
As seen from the side
Path of the surround sound from the
speakers to the listening position
Surround
speakers
Surround back speakers
(1 spkr or 2 spkrs)
60°
Surround
speakers
Surround back
speaker
Point slightly
downwards
Speaker setting examples
Here we describe a number of speaker settings for different purposes. Use these examples as guides to set up
your system according to the type of speakers used and the main usage purpose.
1. DTS-ES compatible system (using surround back speakers)
(1) Basic setting for primarily watching movies
This is recommended when mainly playing movies and using regular single way or 2-way speakers for
the surround speakers.
Surround speaker
Surround back
speaker
Point slightly
downwards
Front speaker
60 to 90 cm
As seen from the side
• Set the front speakers with their front surfaces
as flush with the TV or monitor screen as
possible. Set the center speaker between the
front left and right speakers and no further
from the listening position than the front
speakers.
• Consult the owner’s manual for your
subwoofer for advice on placing the
subwoofer within the listening room.
• If the surround speakers are direct-radiating
(monopolar) then place them slightly behind and at an angle to the listening
position and parallel to the walls at a position 60 to 90 centimeters above
ear level at the prime listening position.
2. When not using surround back speakers
Subwoofer
Surround speaker
Front speaker
60 to 90 cm
Surround speakers
120°
Front speakers
60°
Monitor
Center speaker
As seen from above
As seen from the side
2 Dolby Digital and Dolby Pro Logic
Comparison of home surround
systems
No. recorded channels (elements)
No. playback channels
Playback channels (max.)
Audio processing
High frequency playback limit of
surround channel
Dolby Digital
5.1 ch
5.1 ch
L, R, C, SL, SR, SW
Digital discrete processing Dolby Digital
encoding/decoding
20 kHz
Dolby Pro Logic
2 ch
4 ch
L, R, C, S (SW - recommended)
Analog matrix processing Dolby
Surround
7 kHz
2 Dolby Digital compatible media and playback methods
Marks indicating Dolby Digital compatibility: .
The following are general examples. Also refer to the player’s operating instructions.
Media
LD (VDP)
DVD
Others
(satellite broadcasts, CATV, etc.)
Dolby Digital output jacks
Coaxial Dolby Digital RF output jack
1
Optical or coaxial digital output
(same as for PCM) 2
Optical or coaxial digital output
(same as for PCM)
Playback method (reference page)
Set the input mode to “AUTO”.
(Page 17)
Set the input mode to “AUTO”.
(Page 17)
Set the input mode to “AUTO”.
(Page 17)
Surround
The AVR-2802 is equipped with a digital signal processing circuit that lets you play program sources in the
surround mode to achieve the same sense of presence as in a movie theater.
Dolby Surround
(1) Dolby Digital
Dolby Digital is the multi-channel digital signal format developed by Dolby Laboratories.
Dolby Digital consists of up to “5.1” channels - front left, front right, center, surround left, surround right,
and an additional channel exclusively reserved for additional deep bass sound effects (the Low Frequency
Effects – LFE – channel, also called the “.1” channel, containing bass frequencies of up to 120 Hz).
Unlike the analog Dolby Pro Logic format, Dolby Digital’s main channels can all contain full range sound
information, from the lowest bass, up to the highest frequencies – 22 kHz. The signals within each channel
are distinct from the others, allowing pinpoint sound imaging, and Dolby Digital offers tremendous dynamic
range from the most powerful sound effects to the quietest, softest sounds, free from noise and distortion.