**
*
*
*
*
Specifications
Dimensions
Engine
Dimensions
Engine
Model
Description code
Length Width
Height
Dry mass [weight]
Engine type
Displacement
Bore Stroke
Net power
Max. Net torque
Fuel tank capacity
Engine oil capacity
Cooling system
Ignition system
PTO shaft rotation
Model
Description code
Length Width
Height
Dry mass [weight]
Engine type
Displacement
Bore Stroke
Net power
Max. Net torque
Fuel tank capacity
Engine oil capacity
Cooling system
Ignition system
PTO shaft rotation
The power rating of the engine indicated in this document is the
net power output tested on a production engine for the engine
model and measured in accordance with SAE J1349 at 3,600
rpm (Net Power) and at 2,500 rpm (Max. Net Torque). Mass
production engines may vary from this value.
Actual power output for the engine installed in the final machine
will vary depending on numerous factors, including the
operating speed of the engine in application, environmental
conditions, maintenance, and other variables.
The power rating of the engine indicated in this document is the
net power output tested on a production engine for the engine
model and measured in accordance with SAE J1349 at 3,600
rpm (Net Power) and at 2,500 rpm (Max. Net Torque). Mass
production engines may vary from this value.
Actual power output for the engine installed in the final machine
will vary depending on numerous factors, including the
operating speed of the engine in application, environmental
conditions, maintenance, and other variables.
Specifications may vary according to the types, and are subject to
change without notice.
Forced air
Transistor magneto
Counterclockwise
2.7 kW (3.7 PS)/3,600 rpm
7.4 N·m (0.75 kgf·m)/2,500 rpm
330 369 315 mm
(13.0 14.5 12.4 in)
11.2 kg (24.7 lbs)
135 cm
(8.2 cu-in)
1.3 L (0.29 lmp gal)
0.58 L (0.51 lmp qt)
GC135E
GCAAE
64.0 42.0 mm (2.5 1.7 in)
GC160E
GCABE
337 369 331 mm
(13.3 14.5 13.0 in)
11.5 kg (25.4 lbs)
4-stroke, overhead cam, 1 cylinder
160 cm (9.8 cu-in)
64.0 50.0 mm (2.5 2.0 in)
3.4 kW (4.6 PS)/3,600 rpm
9.4 N·m (0.96 kgf·m)/2,500 rpm
1.8 L (0.40 lmp gal)
0.58 L (0.51 lmp qt)
Forced air
Transistor magneto
Counterclockwise
4-stroke, overhead cam, 1 cylinder
(in accordance with SAE J1349 )
(in accordance with SAE J1349 )
(in accordance with SAE J1349 )
(in accordance with SAE J1349 )
× × ×
× × × ×
× ×
× × ×
× × × ×
× ×
−
TAKING CARE OF UNEXPECTED PROBLEMS TECHNICAL INFORMATION
ENGINE WILL
NOT START
Possible Cause Correction
ENGINE LACKS
POWER
Possible Cause Correction
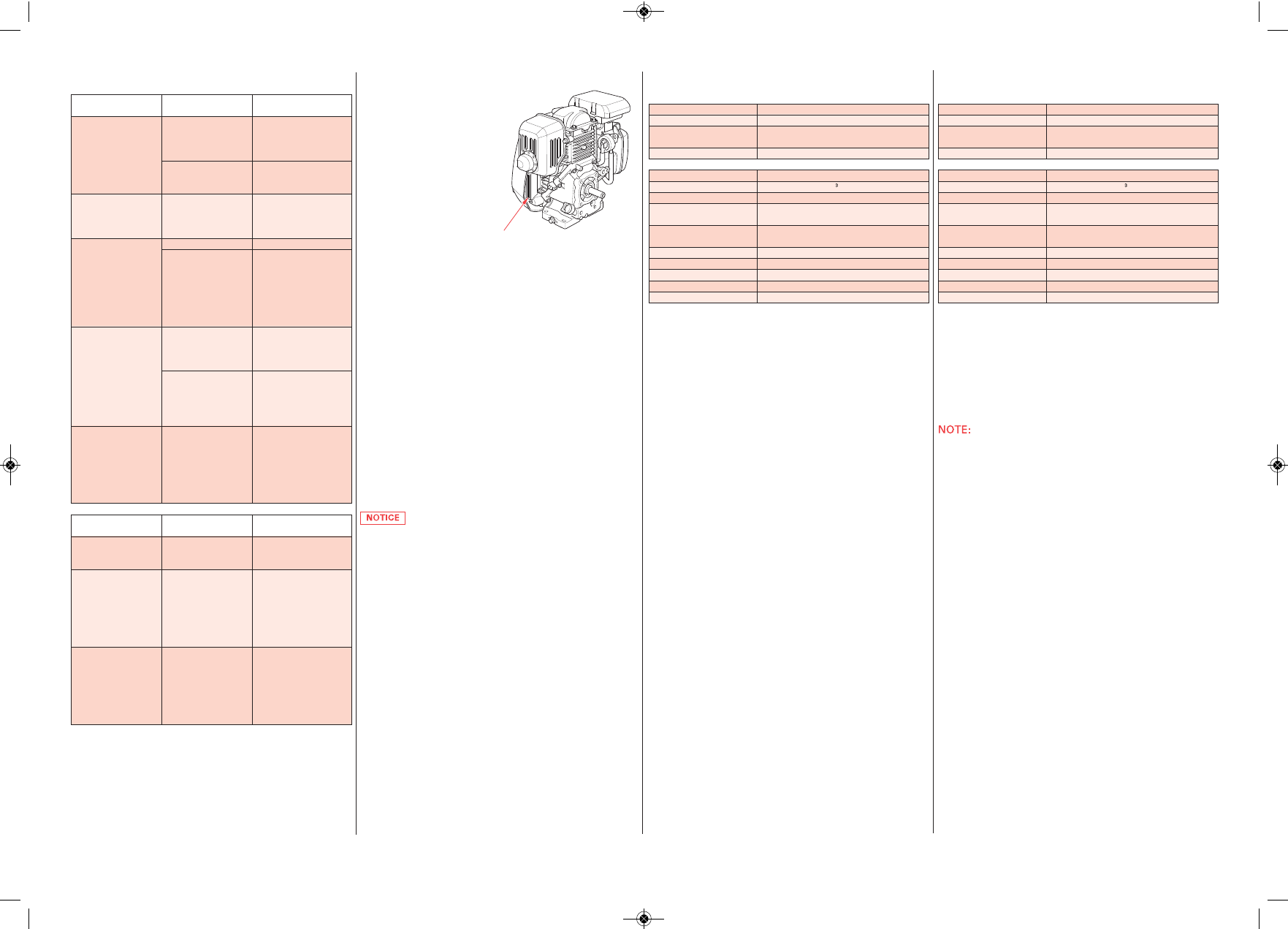
Serial Number Location
Carburetor Modifications for High Altitude Operation
SERIAL NUMBE R &
ENGINE TYPE
Check control
positions.
Check engine
oil level.
Check fuel.
Remove and
inspect spark
plug.
Take engine to
an authorized
Honda
servicing
dealer, or refer
to shop
manual.
Check air filter.
Check fuel.
Take engine to
an authorized
Honda
servicing
dealer, or refer
to shop
manual.
Filter element(s)
restricted.
Bad fuel; engine
stored without
treating or
draining
gasoline, or
refueled with
bad gasoline.
Fuel filter
restricted,
carburetor
malfunction,
ignition
malfunction,
valves stuck, etc.
Clean or replace
filter element(s)
(p. 5).
Drain fuel tank and
carburetor (p. 6).
Refuel with fresh
gasoline (p. 4).
Replace or repair
faulty components
as necessary.
Record the engine serial
number in the space below. You
will need this information when
ordering parts and when
making technical or warranty
inquiries.
Engine type: ___ ___ ___ ___
Engine serial number: __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __
Date Purchased: ______ / ______ / ______
At high altitude, the standard carburetor air-fuel mixture will be
excessively rich. Performance will decrease, and fuel consumption
will increase.
High altitude performance can be improved by specific
modifications to the carburetor. If you always operate your engine
at altitudes above 1,500 meters, have your servicing dealer
perform this carburetor modification.
Even with carburetor modification, engine horsepower will
decrease about 3.5% for each 300 meters increase in altitude. The
effect of altitude on horsepower will be greater than this if no
carburetor modification is made.
Operation of the engine at an altitude lower than the carburetor is
jetted for may result in reduced performance, overheating, and
serious engine damage caused by an excessively lean air/fuel
mixture.
Move rod to
CLOSED position
unless the engine
is warm.
Move lever to
proper position.
Fill with the
recommended oil
to the proper level
(p. 4).
Refuel (p. 4).
Drainfueltankand
carburetor (p. 6).
Refuel with fresh
gasoline (p. 4).
Gap or replace
spark plug (p. 5).
Dry and reinstall
spark plug. Start
engine with control
lever in MAX.
position.
Replace or repair
faulty components
as necessary.
Choke OPEN.
Control lever is
notinproper
position.
Engine oil level
low (Oil Alert
models).
Out of fuel.
Bad fuel; engine
stored without
treating or
draining
gasoline, or
refueled with
bad gasoline.
Spark plug faulty,
fouled, or
improperly
gapped.
Spark plug wet
with fuel
(flooded engine).
Fuel filter
restricted,
carburetor
malfunction,
ignition
malfunction,
valves stuck, etc.
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
1.
2.
3.