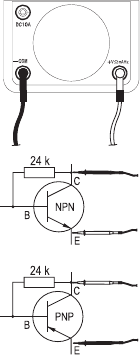
33
g) Transistor test
The transistor test measures the amplification factor of transistors. The amplification factor is the collec-
tor current (IC)/base current (IB) ratio. This function requires an auxiliary circuit with a resistor of 24 kilo-
ohm (not included in delivery). Connect this resistor between the base and the collector connection of
the transistor.
Proceed as follows to measure the amplification factor:
- Use the rotary switch to select the measuring function Ω and the
measuring range “x10/15mA”.
- Connect the black measuring line with the COM socket (6) and
the red measuring line with the V/Ω socket (7).
- Now perform null balancing.
- Connect the two test prods with each other and wait until the
pointer has stabilised. A value of approx. 0 Ohm must be dis-
played. In case of a deviation, adjust the pointer to 0 Ohm using
the 0 Ohm calibration control (9).
- Now connect the two test prods with the test object (transistor),
depending on the transistor type.
NPN: Black measuring line at collector (C), red measuring line at
emitter (E)
PNP: Red measuring line at collector (C), black measuring line at
emitter (E)
- Read off the measuring value for the amplification factor on the
“hFE” scale.
- If there is no display, the transistor is measured in reverse direction or the transistor is defective
(break).
- After measuring, put the rotary switch in the “OFF” position to turn off the multimeter.
☞
If the base connection of the transistor is open (no resistor used), the leakage current “Iceo”
between collector and emitter is displayed. The value can be read off on the “Iceo” scale,
the unit being mA.
h) Frequency measurement
ƽ
Make sure you do not exceed the permitted max. input value of 10V/AC.
The multimeter can measure frequencies from 0 Hz to 25 kHz in the voltage from 2.5 to 10 V/AC.