7271
Etherfast
®
Wireless AP + Cable/DSL Router with PrintServer
1. At the DOS command prompt, type “ping -a 24.53.32.4”, where
24.53.32.4 is the IP address you just pinged. Information such as the fol-
lowing data will be displayed.
(Please note that the screen displayed below is only an example and may
appear differently on your system.)
C:\>ping -a 24.53.32.4
Pinging mail.msnv3.occa.home.com [24.53.32.4] with 32
bytes of data:
Reply from 24.53.32.4: bytes=32 time<10ms TTL=127
Reply from 24.53.32.4: bytes=32 time<10ms TTL=127
Reply from 24.53.32.4: bytes=32 time<10ms TTL=127
Reply from 24.53.32.4: bytes=32 time<10ms TTL=127
Ping statistics for 24.53.32.4:
Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 4, Lost = 0 (0%
loss),
Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds:
Minimum = 0ms, Maximum = 0ms, Average = 0ms
2. Write down the web address returned by the ping command. (In the
example above: mail.msnv3.occa.home.com.) This web address is the web
address assigned to the IP address you just pinged. While the IP address of
“mail” could conceivably change, it is likely that this web address will not.
3. Replace your ISP’s abbreviated server address with this extended web
address in the corresponding Internet application (web browser, e-mail
application, etc.).
Once you have replaced the brief server address with the true server address,
the Router should have no problem accessing the Internet through that Internet
application.
Follow these instructions to install the TCP/IP Protocol on one of your PCs only
after a network card has been successfully installed inside the PC. These
instructions are for Windows 95, 98, and Millennium. For TCP/IP setup under
Windows NT or 2000, please refer to your Windows manual.
Installing the TCP/IP Protocol
Instant Broadband
TM
Series
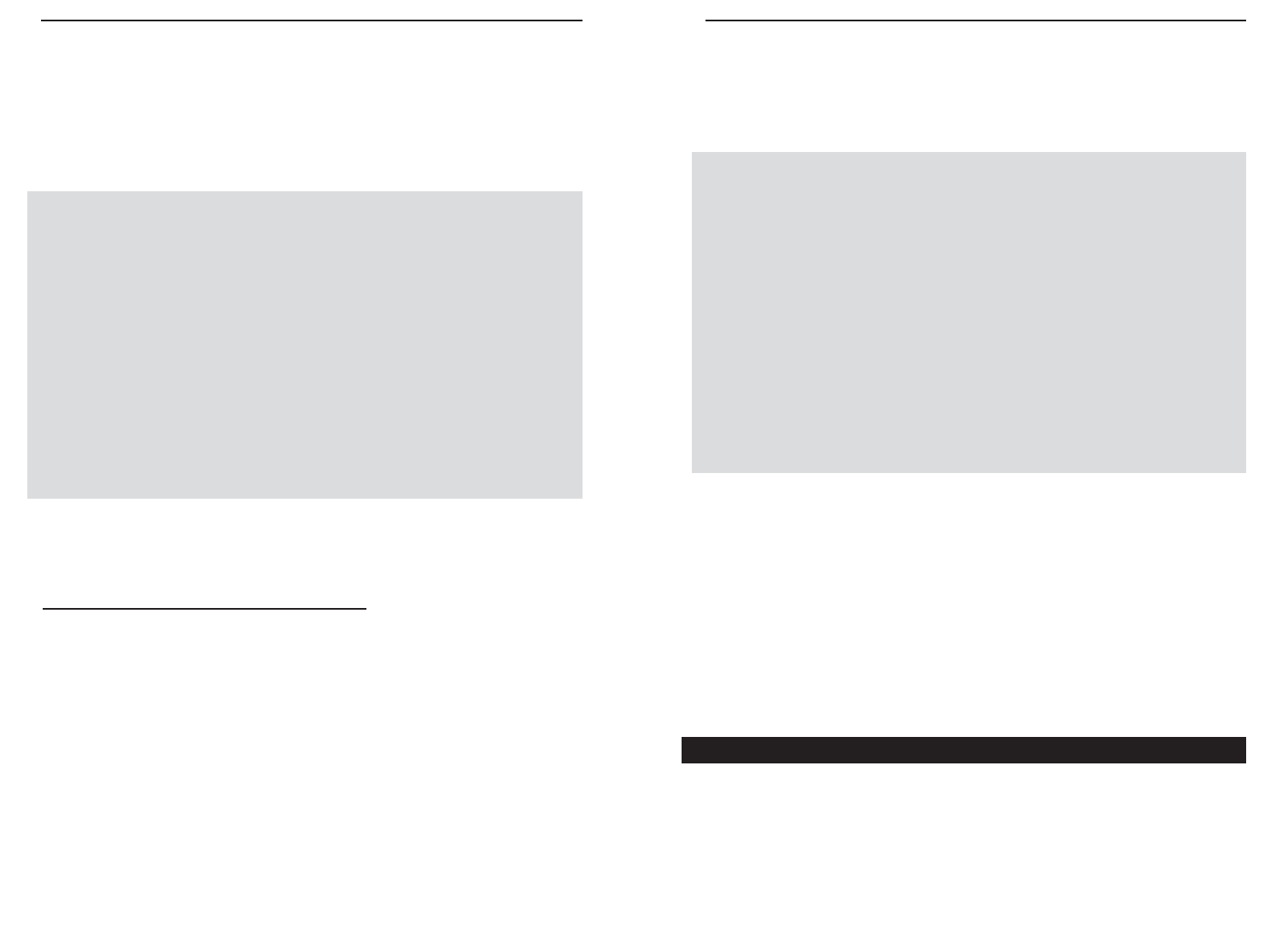
3. At the DOS command prompt, type "ping mail" (assuming that the loca-
tion for which you’re trying to find an IP address is configured as “mail”).
Press Enter. Information such as the following data, taken from a ping of
Microsoft Network’s e-mail server, will be displayed.
(Please note that the screen displayed below is only an example and may
appear differently on your system.)
C:\>ping mail
Pinging mail [24.53.32.4] with 32 bytes of data:
Reply from 24.53.32.4: bytes=32 time<10ms TTL=128
Reply from 24.53.32.4: bytes=32 time<10ms TTL=128
Reply from 24.53.32.4: bytes=32 time<10ms TTL=128
Reply from 24.53.32.4: bytes=32 time<10ms TTL=128
Ping statistics for 24.53.32.4:
Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 4, Lost = 0 (0%
loss),
Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds:
Minimum = 0ms, Maximum = 0ms, Average = 0ms
4. Write down the IP address returned by the ping command. (In the
example above: 24.53.32.4.) This IP address is the actual IP address of the
server “mail”, or any other word or value you have pinged.
Step Two: Pinging for a Web Address
While the IP address returned above would work as your e-mail server address,
it may not be permanent. IP Addresses change all the time. Web addresses,
however, usually don’t. Because of this, you’re likely to have less problems by
configuring your system with web addresses rather than IP addresses. Follow
the instructions below to find the web address assigned to the IP address you
just pinged.