66
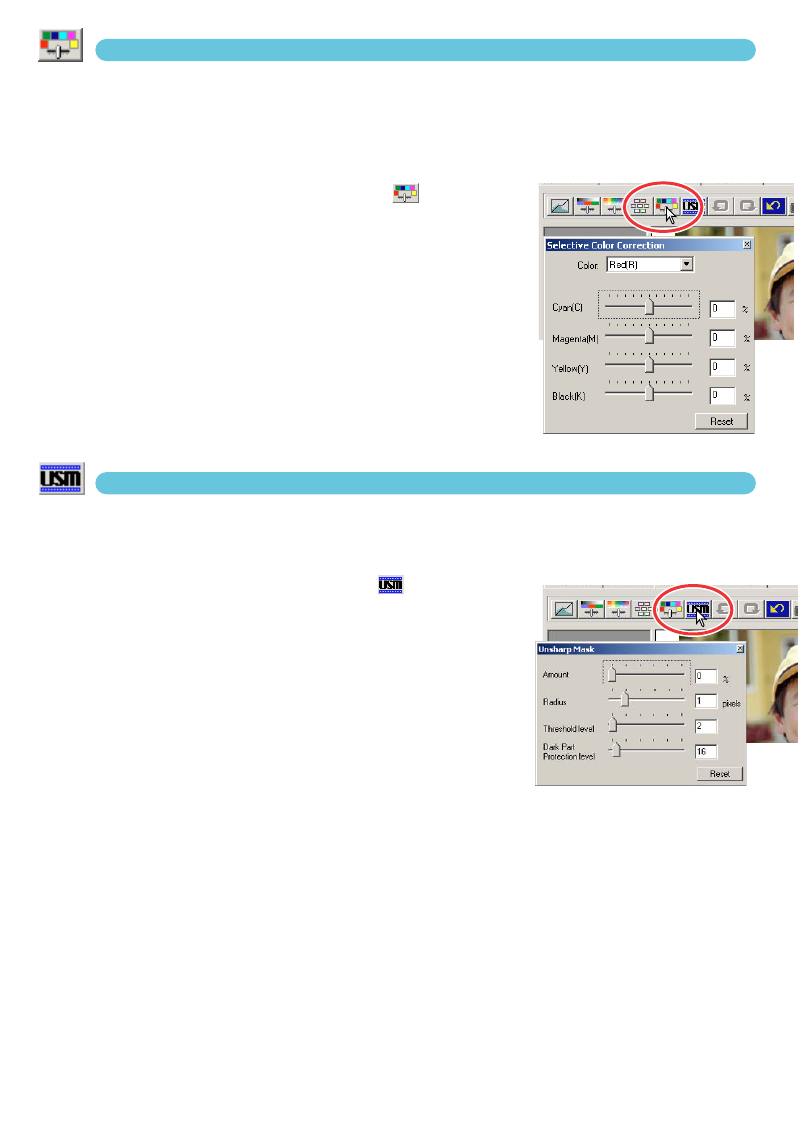
SELECTIVE-COLOUR CORRECTIONS
Selective-colour correction is an advanced technique to refine the colours in the image. The colour
of each process colour, cyan, magenta, yellow, and black, can be used to adjust the six separate
colour groups in the image: red, green, blue, cyan, magenta, and yellow. This type of correction is
effective in changing a specific colour without influencing any of the other colours in the image. For
example, if the sky looks purplish instead of blue, magenta can be reduced in the blue colour group.
1 Click the selective-colour button .
2 Click the arrow next to the colour list box to
select the colour group.
3 Drag a slider or enter a value in a text box to
adjust the selected colour.
• More than one slider can be used to adjust the selected
colour.
• Changes will be reflected in the prescan image.
• Click the reset button to cancel any changes.
UNSHARP MASK
The unsharp mask sharpens edges in the image without affecting overall image contrast. This mask
can be used with soft or slightly out-of-focus images. The effect of the unsharp mask is very subtle,
but makes a significant improvement to the overall appearance of the image.
1 Click the unsharp-mask button .
• The unsharp-mask dialog box appears.
2 Drag a slider or enter a value in a text box to
adjust the parameters of the mask.
• The effect of the unsharp mask cannot be viewed in the pres-
can image. It will only be seen in the final scan.
• The result of the unsharp mask differs with image resolution.
Make several scans with slight changes to the settings until
the settings produce the intended result.
• Clicking the reset button restores the default settings.
• Amount: can be adjusted between 0% and 500%. Adjust the slider to increase level of con-
trast. If the value is too high, pixelation (the image becomes noticeably rough or grainy) will
be apparent. 150% to 200% is recommended for high quality printed images.
• Radius: can be adjusted between 0.1 and 5. The default setting is 1. Adjust the slider to
increase the edge sharpness of the pixels. 1 to 2 is recommended for high quality printed
images. Changes to the radius are more apparent on printed images, than images displayed
on a monitor.
• Threshold level: can be adjusted between 0 and 255. The default setting is 2. If the differ-
ence between the surrounding pixels is greater than the threshold level, that pixel is recog-
nised as a sharp subject pixel. When the level is set to 0, the whole image is corrected. The
threshold level can separate smooth or even areas from edges and detailed areas to be
sharpened.